You need to know what kind of tech is underpinning your electric vehicles and there is a lot of tech to look at, today we want to examine the two different kinds of motors that turn your wheels.
The difference we are talking about is in the way the magnetic field is arranged and how it can affect the performance of the motor. One type of motor arranges the magnetic field perpendicular to the axis while the other arranges it parallel to the axis

Note: This is quite a comprehensive and long article but if you just want the bullet points, please go right to the end of the article.
An axial flux motor is a type of electric motor that uses an axial flux configuration, meaning that the flux (or flow) of the magnetic field is aligned parallel to the central axis of the motor. This is in contrast to a radial flux motor, which has a magnetic field that is aligned perpendicular to the central axis of the motor.
Axial flux motors have several advantages over radial flux motors, including a smaller size, lighter weight, and higher power density. They are also more efficient at high speeds and have a higher power-to-weight ratio.
Axial flux motors are used in a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, drones, and wind turbines. They are also used in some portable power tools and other small, portable devices.
There are two main types of axial flux motors: interior permanent magnet (IPM) motors and exterior permanent magnet (EPM) motors. IPM motors have the magnets located inside the rotor, while EPM motors have the magnets located outside the rotor. Both types of axial flux motors have their own unique advantages and are used in different types of applications.
Why are axial flux motors more powerful

In a radial flux motor, the magnets are typically arranged in a circular pattern around the perimeter of the rotor, which is the rotating part of the motor. The rotor is typically cylindrical in shape, and the magnets are arranged in a circular pattern around the circumference of the rotor.
In an axial flux motor, the magnets are typically arranged in a flat, disc-like shape, with the magnetic field aligned parallel to the central axis of the motor. The magnets are typically arranged in alternating north and south pole configurations, with the north and south poles facing each other across the central axis of the motor.
Why are axial flux motors more powerful than radial flux motors?
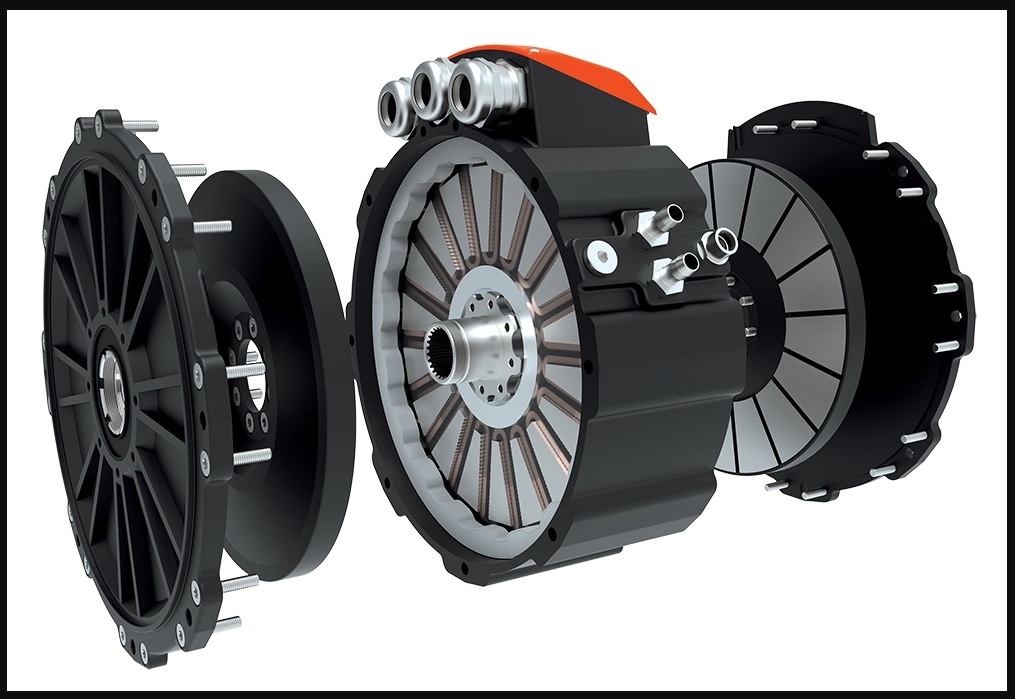

Axial flux motors are generally more powerful than radial flux motors for several reasons.
One reason is that axial flux motors have a higher power density, which means that they can produce more power in a smaller size. This is because the magnetic field in an axial flux motor is aligned parallel to the central axis of the motor, which allows the rotor and stator to be positioned closer together. This results in a smaller, more compact motor with a higher power output.
Another reason is that axial flux motors are more efficient at high speeds. This is because the magnetic field in an axial flux motor is better able to follow the movement of the rotor at high speeds, which results in less energy loss. This allows axial flux motors to produce more power at high speeds compared to radial flux motors.
Finally, axial flux motors have a higher power-to-weight ratio, which means that they can produce more power relative to their weight. This is due in part to their smaller size and lighter weight, which allows them to be more nimble and responsive than heavier motors.
Overall, the combination of a higher power density, higher efficiency at high speeds, and a higher power-to-weight ratio makes axial flux motors more powerful than radial flux motors in many applications.
Are axial flux motors more durable than radial flux motors
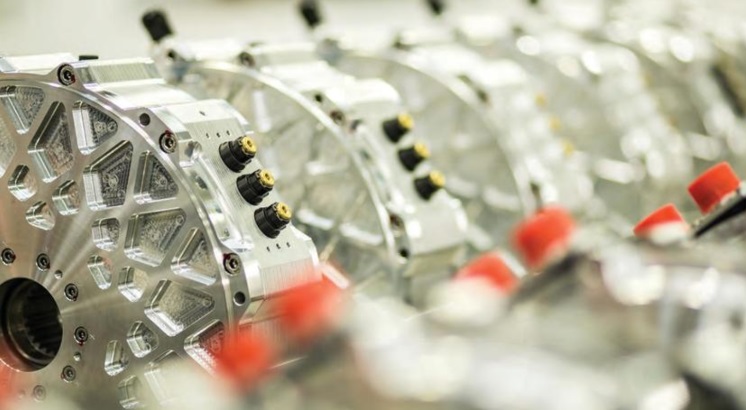

There is no definitive answer to whether axial flux motors are more durable than radial flux motors, as the durability of a motor depends on a number of factors, including the quality of the materials used, the manufacturing process, and the operating conditions.
In general, both axial flux motors and radial flux motors can be highly durable and reliable, and both types of motors are used in a variety of applications where durability is important.
That being said, there are some advantages to axial flux motors that could potentially make them more durable in certain applications. For example, axial flux motors have a higher power density, which means that they can produce more power in a smaller size. This can result in less mechanical stress on the motor, which could potentially improve its durability.
Additionally, axial flux motors are more efficient at high speeds, which means that they generate less heat and have less energy loss. This could potentially lead to longer lifespan for the motor, as heat is one of the main causes of wear and tear in motors.
Overall, it is difficult to say definitively whether axial flux motors or radial flux motors are more durable, as it depends on the specific application and operating conditions. Both types of motors can be highly durable and reliable when properly designed and maintained.
Are axial flux motors more expensive to manufacture?

It is difficult to say definitively whether axial flux motors are more expensive to manufacture than radial flux motors, as the cost of manufacturing a motor depends on a number of factors, including the materials used, the complexity of the design, and the volume of production.
In general, axial flux motors may be more expensive to manufacture than radial flux motors due to their more complex design. Axial flux motors have a magnetic field that is aligned parallel to the central axis of the motor, which requires more precise manufacturing processes and higher quality materials to ensure proper performance.
On the other hand, radial flux motors have a simpler design, with a magnetic field that is aligned perpendicular to the central axis of the motor. This makes them easier and less expensive to manufacture in some cases.
Overall, the cost of manufacturing axial flux motors and radial flux motors can vary widely depending on the specific design and production requirements. It is difficult to make generalizations about the relative cost of manufacturing these two types of motors.
Why aren’t all EV motors axial flux if it has so many advantages

There are a few reasons why axial flux motors are not more widely used in electric vehicles:
- Manufacturing complexity: Axial flux motors have more complex stators because they have a multi-layered winding structure, which can make them more difficult and expensive to manufacture.
- Efficiency: While axial flux motors can be more efficient than radial flux motors in certain applications, this is not always the case. The relative efficiency of an electric motor depends on many factors, including the specific design and operating conditions.
- Torque density: Axial flux motors tend to have lower torque density compared to radial flux motors, which can limit their power output and make them less suitable for certain high-performance applications.
- Cost: Radial flux motors are more widely used and have been around for longer, so they are generally less expensive to produce. This can make them a more cost-effective choice for electric vehicle manufacturers.
Overall, there are trade-offs between different types of electric motors, and the best choice for a given application will depend on the specific requirements and constraints of that application.
What are the drawbacks of axial flux motors?
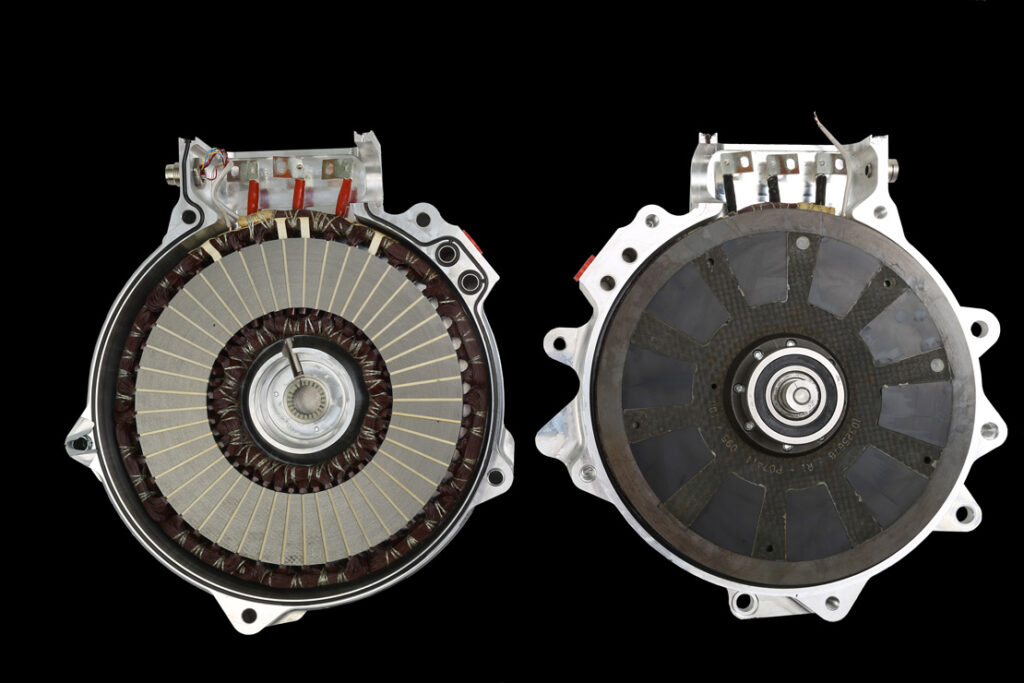
There are a few potential drawbacks to using axial flux motors:
Complexity: Axial flux motors have a more complex design than radial flux motors, which can make them more difficult and expensive to manufacture. This complexity can also make axial flux motors more challenging to repair and maintain.
Limited power range: Axial flux motors are generally more efficient at high speeds and have a higher power density than radial flux motors, but they may not be as effective at lower speeds. This can limit their use in some applications where low-speed torque is important.
Limited size range: Axial flux motors are generally smaller and more lightweight than radial flux motors, but they may not be available in as large a size range. This can limit their use in some applications where a larger motor is required.
Noise and vibration: Axial flux motors may produce more noise and vibration than radial flux motors due to their more complex design and higher operating speeds. This can be an issue in some applications where low noise and vibration levels are important.
Overall, while axial flux motors have some advantages over radial flux motors, they also have some potential drawbacks that need to be considered when choosing a motor for a specific application.
Which type of motor is more common in electric cars and why?

Both axial flux motors and radial flux motors are used in electric vehicles, and the specific type of motor that is used can depend on a variety of factors, including the size and power requirements of the vehicle, the desired performance characteristics, and the cost of manufacturing.
In general, axial flux motors are more commonly used in electric vehicles due to their high power density, efficiency at high speeds, and high power-to-weight ratio. These characteristics make them well-suited to electric vehicle applications, where high performance and efficiency are important.
Radial flux motors are also used in some electric vehicles, particularly in applications where low-speed torque is important or where a larger motor is required. Radial flux motors have a simpler design and may be less expensive to manufacture than axial flux motors in some cases, which can make them an attractive option in certain applications.
Overall, both axial flux motors and radial flux motors have their own unique advantages and can be well-suited to different types of electric vehicle applications. The specific type of motor that is used can depend on a variety of factors and may vary from one vehicle to another.
Tesla uses axial or radial flux motors?
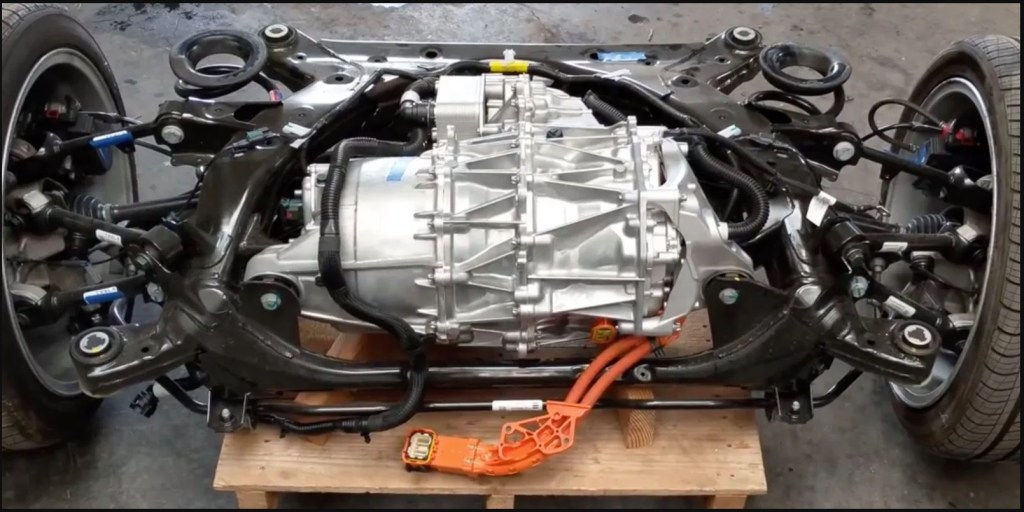

Tesla uses axial flux motors in some of its electric vehicles. Axial flux motors are well-suited to electric vehicle applications due to their high power density, efficiency at high speeds, and high power-to-weight ratio.
One example of a Tesla electric vehicle that uses an axial flux motor is the Tesla Model 3. The Model 3 is equipped with a dual motor drivetrain that includes an axial flux motor on the rear axle. This provides the Model 3 with all-wheel drive capability and helps to improve its performance and handling.
In addition to the Model 3, Tesla has also used axial flux motors in other electric vehicle models, including the Tesla Roadster, the Tesla Model S, and the Tesla Model X. These vehicles have all benefited from the use of axial flux motors, which have helped to improve their performance and make them more efficient.
Overall, Tesla’s use of axial flux motors in its electric vehicles has helped the company to produce some of the most advanced and high-performing electric vehicles on the market.
Does the hyundai use axial or radial flux motors in their ev
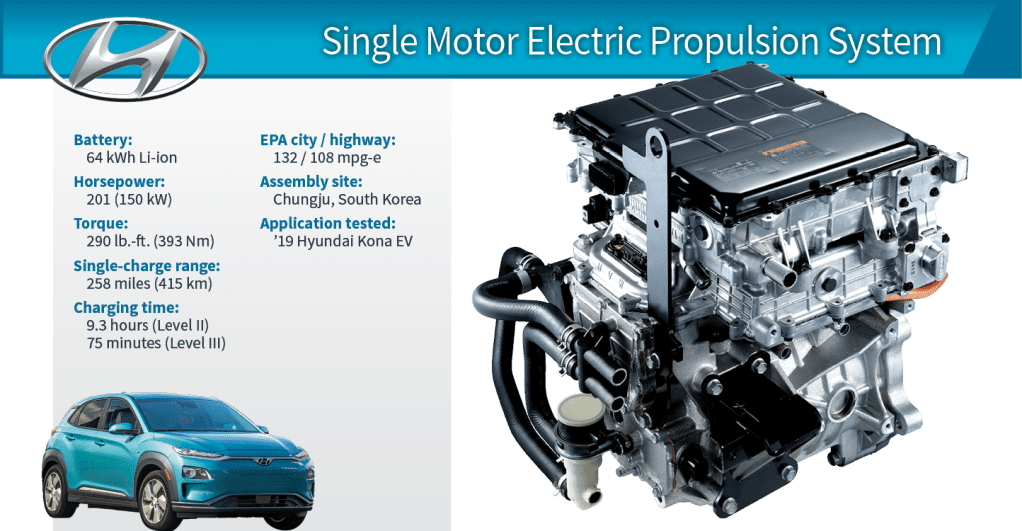
It is likely that Hyundai uses both axial flux motors and radial flux motors in its electric vehicles, as both types of motors have their own unique advantages and can be well-suited to different types of electric vehicle applications.
For example, Hyundai’s Kona Electric, which is a compact SUV, is equipped with a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) that uses an axial flux configuration. This motor is capable of producing up to 201 horsepower and is paired with a high-capacity 64 kWh lithium-ion battery pack, which provides the Kona Electric with a range of up to 258 miles (415 km) on a single charge.
Other Hyundai electric vehicles, such as the Hyundai Ioniq Electric and the Hyundai Nexo, may also use axial flux motors or radial flux motors, depending on the specific requirements of the vehicle.
Overall, the specific type of motor that is used in a Hyundai electric vehicle can depend on a variety of factors, including the size and power requirements of the vehicle, the desired performance characteristics, and the cost of manufacturing. Both axial flux motors and radial flux motors have their own unique advantages and can be well-suited to different types of electric vehicle applications.
What are some vehicles that use radial flux motors?
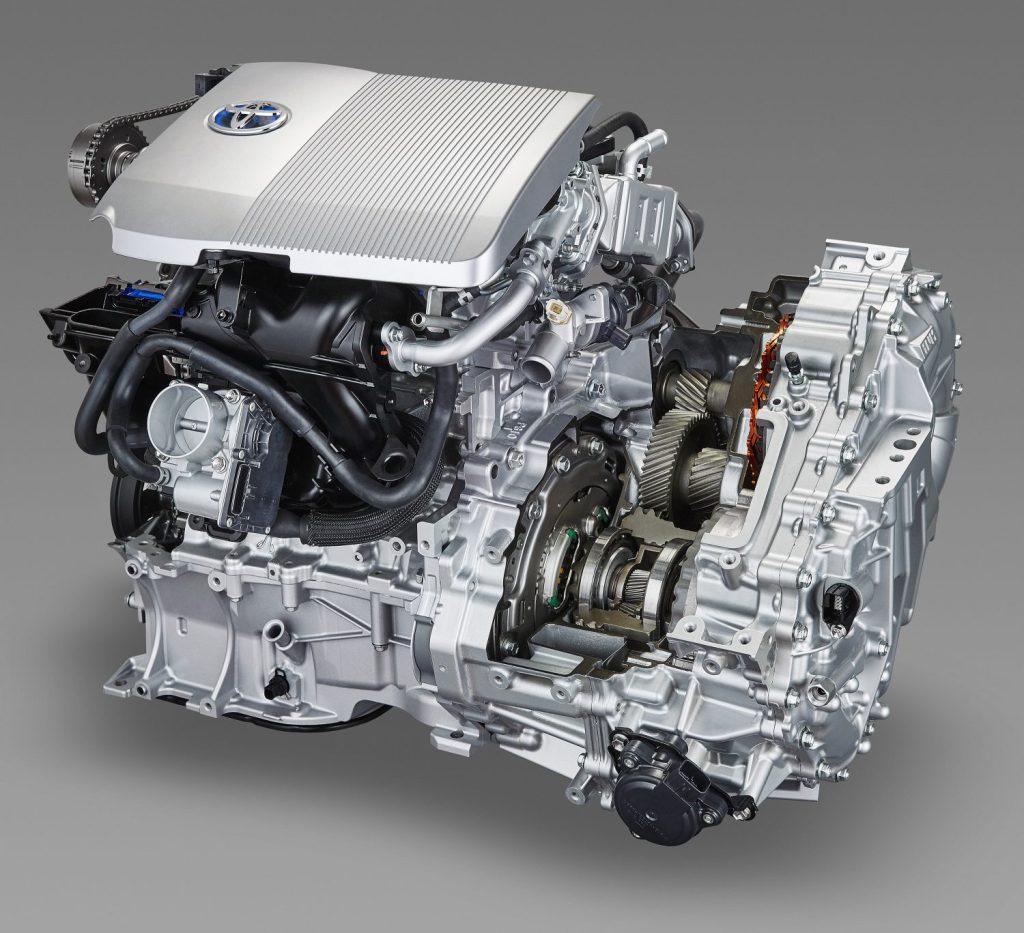

There are a number of electric vehicles that use radial flux motors, including:
Toyota Prius Prime: The Toyota Prius Prime is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle that uses a radial flux motor as part of its hybrid drive system. The motor is capable of producing up to 53 horsepower and is paired with a 1.8-liter four-cylinder gasoline engine and a high-capacity 8.8 kWh lithium-ion battery pack.
BMW i3: The BMW i3 is a fully electric vehicle that uses a radial flux motor to power the rear wheels. The motor is capable of producing up to 168 horsepower and is paired with a high-capacity 42.2 kWh lithium-ion battery pack, which provides the i3 with a range of up to 153 miles (246 km) on a single charge.
Nissan Leaf: The Nissan Leaf is a fully electric vehicle that uses a radial flux motor to power the front wheels. The motor is capable of producing up to 110 horsepower and is paired with a high-capacity 40 kWh lithium-ion battery pack, which provides the Leaf with a range of up to 149 miles (240 km) on a single charge.
Overall, radial flux motors are used in a variety of electric vehicle applications, and they have their own unique advantages that can make them well-suited to certain types of vehicles.
Which has a higher energy conversion efficiency from electric to kinetic energy, radial flux or axial flux motors?
The energy conversion efficiency of an electric motor refers to the percentage of electrical energy that is converted into useful mechanical energy. In general, both axial flux motors and radial flux motors can have high energy conversion efficiencies, and the specific efficiency of a motor can depend on a number of factors, including the materials used, the design of the motor, and the operating conditions.
That being said, axial flux motors may have a slightly higher energy conversion efficiency than radial flux motors in some cases due to their higher power density and efficiency at high speeds. This is because axial flux motors can produce more power in a smaller size, which can result in less energy loss and higher efficiency.
However, radial flux motors may have a higher energy conversion efficiency than axial flux motors in certain applications where low-speed torque is important. This is because radial flux motors have a simpler design and may be more efficient at lower speeds.
Overall, the energy conversion efficiency of an electric motor can vary widely depending on the specific design and operating conditions, and it is difficult to make generalizations about the relative efficiency of axial flux motors and radial flux motors.
Does that mean radial flux motors are mure suited for heavy vehicle application?
Radial flux motors may be more suited to heavy vehicle applications in some cases due to their ability to produce high levels of low-speed torque. Low-speed torque is a measure of the rotational force that a motor can produce at low speeds, and it is important in heavy vehicle applications where the vehicle may need to start and stop frequently or operate at low speeds for extended periods of time.
Radial flux motors have a simpler design than axial flux motors and may be more efficient at producing low-speed torque. This can make them well-suited to heavy vehicle applications where low-speed torque is important.
However, it is important to note that the suitability of a specific type of motor for a heavy vehicle application depends on a number of factors, including the size and power requirements of the vehicle, the desired performance characteristics, and the cost of manufacturing. Both axial flux motors and radial flux motors have their own unique advantages, and the specific type of motor that is used in a heavy vehicle application can depend on the specific requirements of the vehicle.
Do axial flux motors require different maintenance and care from radial flux motors?

Axial flux motors and radial flux motors may require different maintenance and care, depending on the specific design and operating conditions of the motor. In general, electric motors require regular maintenance to ensure that they are operating at their best and to extend their lifespan.
Some of the general maintenance tasks that may be required for both axial flux motors and radial flux motors include:
Cleaning: Keeping the motor clean can help to prevent the build-up of dirt and debris, which can interfere with the operation of the motor and cause it to wear out more quickly.
Lubrication: Lubricating the moving parts of the motor can help to reduce friction and wear, which can extend the lifespan of the motor.
Inspections: Regular inspections can help to identify potential problems with the motor and allow for timely repairs to be made.
Repairs: When needed, repairs should be made promptly to ensure that the motor is operating at its best and to extend its lifespan.
Overall, the specific maintenance and care requirements for an axial flux motor or radial flux motor can depend on the specific design and operating conditions of the motor. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and to address any problems or issues as they arise.
Here are five key points to consider when comparing radial flux motors and axial flux motors:
- Configuration: Radial flux motors have a magnetic field that is aligned perpendicular to the central axis of the motor, while axial flux motors have a magnetic field that is aligned parallel to the central axis of the motor.
- Size and weight: Axial flux motors are generally smaller and lighter than radial flux motors, which can make them more suitable for applications where size and weight are important considerations.
- Efficiency: Axial flux motors are generally more efficient at high speeds and have a higher power density than radial flux motors, while radial flux motors may be more efficient at lower speeds.
- Power-to-weight ratio: Axial flux motors have a higher power-to-weight ratio than radial flux motors, which means that they can produce more power relative to their weight.
- Cost: The cost of manufacturing axial flux motors and radial flux motors can vary widely depending on the specific design and production requirements, and it is difficult to make generalizations about the relative cost of these two types of motors.
